A network is a set of devices (often referred to as nodes) connected by communication links. A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network.
Distributed Processing:-
Most networks use distributed processing, in which a task is divided among multiple computers. Instead of one single large machine being responsible for all aspects of a process, separate computers (usually a personal computer or workstation) handle a subset.
Type of Topology :-
Mesh Topology:- In a mesh topology, every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device.A mesh offers several advantages over other network topologies. First, the use of dedicated links guarantees that each connection can carry its own data load, thus elimi- nating the traffic problems that can occur when links must be shared by multiple devices. Second, a mesh topology is robust. If one link becomes unusable, it does not incapaci tate the entire system. Third, there is the advantage of privacy or security. When every message travels along a dedicated line, only the intended recipient sees it.

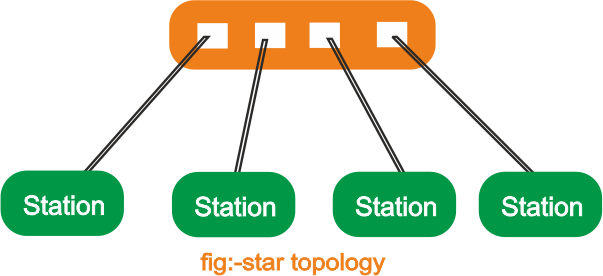
Star Topology:- In a star topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller, usually called a hub. A star topology is less expensive than a mesh topology. In a star, each device needs only one link and one I/O port to connect it to any number of others. This factor also makes it easy to install and reconfigure. Far less cabling needs to be housed, and additions, moves, and deletions involve only one connection: between that device and the hub. Other advantages include robustness. If one link fails, only that link is affected. AJI other links remain active. This factor also lends itself to easy fault identification and fault isolation. As long as the hub is working, it can be used to monitor link problems and bypass defective links. One big disadvantage of a star topology is the dependency of the whole topology on one single point, the hub. If the hub goes down, the whole system is dead. Although a star requires far less cable than a mesh, each node must be linked to a central hub. For this reason, often more cabling is required in a star than in some other topologies (such as ring or bus). The star topology is used in local-area networks (LAN),
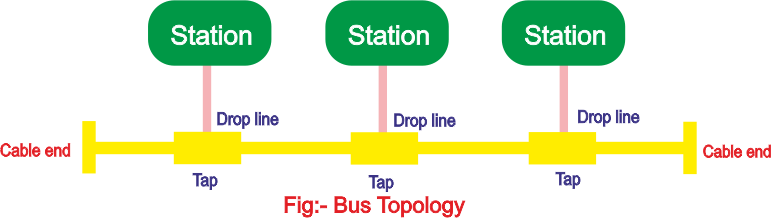
Bus Topology:- A bus topology, on the other hand, is multipoint. One long cable acts as a backbone to link all the devices in a network. Nodes are connected to the bus cable by drop lines and taps. A drop line is a con- nection running between the device and the main cable. A tap is a connector that either splices into the main cable or punctures the sheathing of a cable to create a contact with the metallic core. As a signal travels along the backbone, some of its energy is transformed into heat. Therefore, it becomes weaker and weaker as it travels farther and farther. For Dis this reason there is a limit on the number of taps a bus can support and on the distance. Advantages of a bus topology include ease of installation. Backbone cable can be laid along the most efficient path, then connected to the nodes by drop lines of various lengths. In this way, a bus uses less cabling than mesh or star topologies. Disadvantages include difficult reconnection and fault isolation. A bus is usually designed to be optimally efficient at installation. It can therefore be difficult to add new devices.
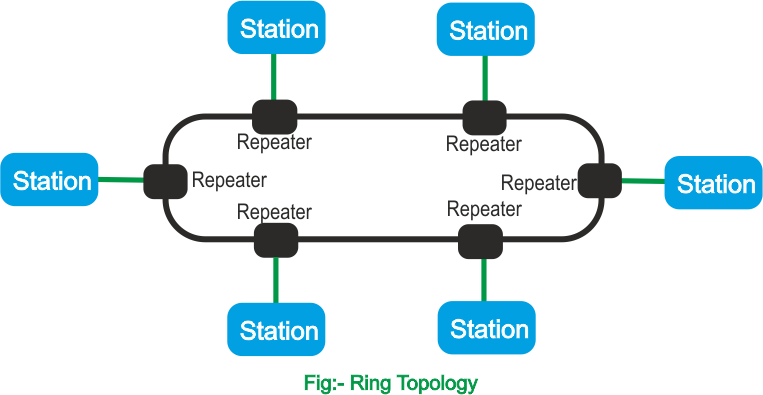
Ring Topology:- In a ring topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it. The only constraints are media and traffic considerations (maximum ring length and number of devices). In addition, fault isolation is simplified Generally in a ring, a signal is circulating at all times. If one device does not receive a signal within a specified period, it can issue an alarm. The alarm alerts the network operator to the problem and its location. However, unidirectional traffic can be a disadvantage. In a simple ring, a break in the ring (such as a disabled station) can disable the entire network. This weakness can be solved by using a dual ring or a switch capable of closing off the break. Ring topology was prevalent when IBM introduced its LAN token ring. Today the need for higher speed LANs has made this topology less popular.